Rima Ninamu
Sustainable supply

![]() FRANCE
FRANCE
Location: Tahiti, French Polynesia
Sector: Agriculture
Date of creation: launched in 2012
Analysis by the association: January 2018
Producer of aquaponics systems.
Overview
In 2012, Teanuanua Teriipaia-Rentier, a young Polynesian with a degree in aquaculture, created his company, Rima Ninamu, specialized in the construction of aquaponic systems mainly for individuals, but also for project promoters and schools.
The main activity of the company is custom construction and installation of aquaponic systems, but it also focused for 5 years on the development of natural inputs to develop low cost production systems. Since 2017, the company also gives trainings to learn all the aquaponics¹ techniques. Thereafter, we will analyze the functioning of the aquaponic systems sold as well as the techniques and natural inputs developed by the company to make these systems optimal, economic and environmentally friendly (we will not analyze the company itself).
- 95% of the income comes from the installation of aquaponic systems.
- Sustainable supply
- Eco-conception
- Responsible consumption
Project operation
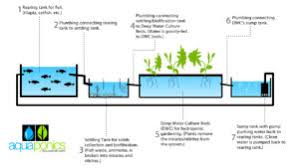
1. Aquaponics system
Natural inputs to fill the mineral deficiencies of plants :
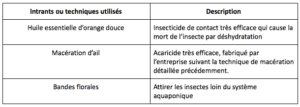
Inputs manufacturing process:
- Macerations consist of leaving organic matter for days or weeks in water to obtain a fertilizer.
Principle:
- anaerobic phase: in a container is introduced organic matter (here seaweed, bananas skinless), then filled with water and sealed with a lid. It is left to macerate 2 weeks.
- aerobic phase: the juice is harvested, diluted to the tenth, and bubbling is added. After three days, the maceration is ready to be used. These macerations are then administered by spraying on the leaves or directly in the water. Tenth dilution is necessary to avoid burning the leaves. Vegetable residues used for maceration (remnants of algae, bananas …) are ultimately used to make compost.
- Vermicomposting: this technique consists of obtaining compost (called vermicompost) from the decomposition of organic matter by earthworms. Here the company supplies earthworms with plant material (green waste). These feed on them and produce droppings. The process is done in a place with a high humidity, it results in a juice enriched by this decomposition that flows through the plant material and is recovered for use as a fertilizer.
Raw material origin:
Algae: available all over the year for free on the beaches of Tahiti. Algae are invasive species, so their use in aquaponics is beneficial for the environment.
Lombrics: imported from New Zealand, but as it is a species that breeds quickly, just import a small amount once
The plants and fish produced:
These systems allow to produce rather green plants, such as salads, Chinese cabbage and herbs. The most common fish are tilapias sunfish, one of the best robust species that reproduces easily. The newborns first pass through the nursery to grow and join the aquaponic system.
Fish Feed:
Fish are fed commercially purchased fish feed. Aquaponic systems are equipped with automatic feeders allowing feeding in the morning and evening. The quantity of food distributed depends on the mass of the fish, but still corresponds to 5% of their biomass.
Inputs to fight against diseases:
Each technique or input is used only in the prevention of diseases and pests, and are administered by foliar sprays.
2. Courses
The company also trains each client on the basics of aquaponics and the basics of using aquaponic systems. Trainings over several weeks are also provided by the company and open to all.
Sustainable approach
- aquaponics is a system which recycles livestock effluents, thus avoiding their release into the environment
- in traditional aquaponics, it is common to add industrial chemical additives, but this system does not use what is better for the environment
- use of algae present on the coast of Tahiti, thus reducing their expansion
- No purchase of additives to overcome mineral deficiencies,
- Tilapia sunfish is a cheap species to produce,
- Few manpower needed to maintain a system but also especially for large areas. (a person can cover 1600 square meters / d)
- a lot of crop rotation so good yields.
- allows the beneficiaries of the system to have a clean food production, and thus to ensure food security and even to be able to generate income through the sale of vegetables and fish
- Rima Ninamu also installs aquaponic systems in middle and high schools serving as a teaching aid to the discovery and understanding of aquaponics
Replicability & future perspectives
Aquaponics in Tahiti is done in a covered structure or in a greenhouse with a lot of ventilation because of the high temperatures. The system is reproducible as is for countries with the same climatic conditions.
Moreover, aquaponics is spreading over the world and is easily replicable anywhere!
- production of fruit plants is difficult because very technical and because the water is too deficient in potassium,
- aquaculture has unfortunately not many opportunities in Tahiti for the moment(price range, interest of the people…)
- one of the challenges in Tahiti: the temperature (one must constantly try to have low temperatures for the well being of the fish).
- such a system can only generate a salary from an operating area of 200 square meters, so that individuals can not fully live on them
The food used to feed the fish is the most costly in the operation of an aquaponic system, which is why Rima Ninamu leads R & D to develop its fly production as an alternative feed for fish. In July 2018, the company will launch its production of black soldier fly (Hermetias illuans) (with valorization of copra cake) to feed the fish of the aquaponic systems. It will also launch its own aquaponic farm on 200 m² in Pirae (Tahiti island). Finally, the company is also in the acquisition phase to launch a hatchery of mangrove crabs.
- Aquaponics¹ = technique combining fish farming and plant culture in hydroponics. This system is a closed circuit, where natural bacterial cycles make it possible to transform the discharges of fish into water into nutrients that can be assimilated by plants.
- Iron chelate² = association between iron and humic or clay substances. This association allows a better assimilation of iron by the plant. Chelation is the process of making iron available to an organism.
